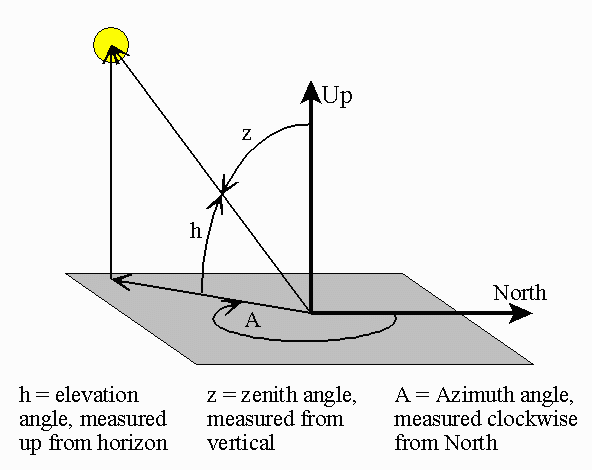
Here is the first raw code. The original R-codelines are commented out.
void CalculateSunPosition(float* azimuth, float *elevation, float latitude, float longitude,
unsigned year, unsigned month, unsigned day, float hour = 12, float minute = 0, float sec = 0)
{
/*
Original R-code at: http://stackoverflow.com/questions/8708048/position-of-the-sun-given-time-of-day-latitude-and-longitude?rq=1
*/
year = Clamp(year, -4713, 5000);
month = Clamp(month, 1, 12);
day = Clamp(day, 1, 31);
hour = Clamp(hour, 0.0f, 23.0f);
minute = Clamp(minute, 0.0f, 59.0f);
sec = Clamp(sec, 0.0f, 59.0f);
latitude = Clamp(latitude, -90.0f, 90.0f);
longitude = Clamp(longitude, -180.0f, 180.0f);
//twopi <-2 * pi
//deg2rad <-pi / 180
//# Get day of the year, e.g.Feb 1 = 32, Mar 1 = 61 on leap years
unsigned month_days[] = { 0, 31, 28, 31, 30, 31, 30, 31, 31, 30, 31, 30 };
//day <-day + cumsum(month.days)[month]
for (unsigned z = 1; z < month;z++) day += month_days[z];
//leapdays <-year %% 4 == 0 & (year %% 400 == 0 | year %% 100 != 0) & day >= 60 & !(month == 2 & day == 60)
// day[leapdays] <-day[leapdays] + 1;
if(year % 4 == 0 && (year % 400 == 0 || year % 100 != 0) && day >= 60 && !(month == 2 && day == 60))
day++;
//# Get Julian date - 2400000
//hour <-hour + min / 60 + sec / 3600 # hour plus fraction
//delta <-year - 1949
//leap <-trunc(delta / 4) # former leapyears
//jd <-32916.5 + delta * 365 + leap + day + hour / 24
hour = hour + minute / 60.0f + sec / 3600.0f;
unsigned delta = year - 1949;
unsigned leap = delta / 4;
double jd = 32916.5f + (double)delta * 365.0 + (double)leap + day + hour / 24.0;
//# The input to the Astronomer's almanach is the difference between
//# the Julian date and JD 2451545.0 (noon, 1 January 2000)
//time <- jd - 51545.
double time = jd - 51545.0;
//# Ecliptic coordinates
//# Mean longitude
//mnlong <-280.460 + .9856474 * time
//mnlong <-mnlong %% 360
//mnlong[mnlong < 0] <-mnlong[mnlong < 0] + 360
double mnlong = 280.460 + .9856474 * time;
mnlong = fmod(mnlong, 360.0);
if (mnlong < 0) mnlong += 360.0;
//mnlong = mnlong * M_DEGTORAD;// mnlong turn to radian
//# Mean anomaly
//mnanom <-357.528 + .9856003 * time
//mnanom <-mnanom %% 360
//mnanom[mnanom < 0] <-mnanom[mnanom < 0] + 360
//mnanom <-mnanom * deg2rad
double mnanom = 357.528 + .9856003 * time;
mnanom = fmod(mnanom, 360.0);
if (mnanom < 0) mnanom += 360.0;
mnanom = mnanom * M_DEGTORAD;
//# Ecliptic longitude and obliquity of ecliptic
//eclong <-mnlong + 1.915 * sin(mnanom) + 0.020 * sin(2 * mnanom)
//eclong <-eclong %% 360
//eclong[eclong < 0] <-eclong[eclong < 0] + 360
//oblqec <-23.439 - 0.0000004 * time
//eclong <-eclong * deg2rad
//oblqec <-oblqec * deg2rad
double eclong = mnlong + 1.915 * sin(mnanom) + 0.020 * sin(2 * mnanom);
eclong = fmod(eclong, 360.0);
if (eclong < 0) eclong += 360.0;
eclong = eclong * M_DEGTORAD;
double oblqec = 23.439 - 0.0000004 * time;
oblqec = oblqec * M_DEGTORAD;
//# Celestial coordinates
//# Right ascension and declination
//num <-cos(oblqec) * sin(eclong)
//den <-cos(eclong)
//ra <-atan(num / den)
//ra[den < 0] <-ra[den < 0] + pi
//ra[den >= 0 & num < 0] <-ra[den >= 0 & num < 0] + twopi
//dec <-asin(sin(oblqec) * sin(eclong))
double num = cos(oblqec) * sin(eclong);
double den = cos(eclong);
double ra = atan(num / den);
if (den < 0) ra += M_PI;
if (den >= 0 && num < 0) ra += 2 * M_PI;
double dec = asin(sin(oblqec) * sin(eclong));
//# Local coordinates
//# Greenwich mean sidereal time
//gmst <-6.697375 + .0657098242 * time + hour
//gmst <-gmst %% 24
//gmst[gmst < 0] <-gmst[gmst < 0] + 24.
double gmst = 6.697375 + .0657098242 * time + hour;
gmst = fmod(gmst, 24.0);
if (gmst < 0) gmst += 24.0;
//# Local mean sidereal time
//lmst <-gmst + long / 15.
//lmst <-lmst %% 24.
//lmst[lmst < 0] <-lmst[lmst < 0] + 24.
//lmst <-lmst * 15. * deg2rad
double lmst = gmst + longitude / 15.0;
lmst = fmod(lmst, 24.0);
if (lmst < 0) lmst += 24.0;
lmst = lmst * 15.0 * M_DEGTORAD;
//# Hour angle
//ha <-lmst - ra
//ha[ha < -pi] <-ha[ha < -pi] + twopi
//ha[ha > pi] <-ha[ha > pi] - twopi
double ha = lmst - ra;
if (ha < -M_PI) ha += (2 * M_PI);
if (ha > M_PI) ha -= (2 * M_PI);
//# Latitude to radians
//lat <-lat * deg2rad
double latitude_R = latitude * M_DEGTORAD;
//# Azimuth and elevation
*elevation = asin(sin(dec) * sin(latitude_R) + cos(dec) * cos(latitude_R) * cos(ha));// <- solar zenith angle!
*azimuth = asin(-cos(dec) * sin(ha) / cos(*elevation));
//# For logic and names, see Spencer, J.W. 1989. Solar Energy. 42(4) : 353
//cosAzPos <-(0 <= sin(dec) - sin(el) * sin(lat))
//sinAzNeg <-(sin(az) < 0)
//az[cosAzPos & sinAzNeg] <-az[cosAzPos & sinAzNeg] + twopi
//az[!cosAzPos] <-pi - az[!cosAzPos]
bool cosAzPos = (0 <= sin(dec) - sin(*elevation) * sin(latitude));
bool sinAzNeg = (sin(*azimuth) < 0);
if (cosAzPos && sinAzNeg) *azimuth += (2 * M_PI);
if (!cosAzPos) *azimuth = M_PI - *azimuth;
//# if (0 < sin(dec) - sin(el) * sin(lat)) {
//# if(sin(az) < 0) az <- az + twopi
//# } else {
// # az <-pi - az
//# }
//el <-el / deg2rad
//az <-az / deg2rad
//lat <-lat / deg2rad
*elevation = *elevation / M_DEGTORAD;
*azimuth = *azimuth / M_DEGTORAD;
//return(list(elevation = el, azimuth = az))
}
And here is the second code “General Solar Position Calculations”.
void GeneralSolarPositionCalc(float* azimuth, float *elevation, float latitude, float longitude, float timezone,
bool daylightsaving, unsigned year, unsigned month, unsigned day,
float hour, float minute = 0, float sec = 0)
{
year = Clamp(year, 2000, 2050);
month = Clamp(month, 1, 12);
day = Clamp(day, 1, 31);
hour = Clamp(hour, 0.0f, 23.0f);
minute = Clamp(minute, 0.0f, 59.0f);
sec = Clamp(sec, 0.0f, 59.0f);
latitude = Clamp(latitude, -90.0f, 90.0f);
longitude = Clamp(longitude, -180.0f, 180.0f);
unsigned month_days[] = { 0, 31, 28, 31, 30, 31, 30, 31, 31, 30, 31, 30 };
for (unsigned z = 1; z < month; z++) day += month_days[z];
//leapday
if (year % 4 == 0 && (year % 400 == 0 || year % 100 != 0) && day >= 60 && !(month == 2 && day == 60))
day++;
// latitude (radian)
float lat_rad = latitude * M_DEGTORAD;
//fract of year (radian)
float gamma = (day - 1.0f + (hour - 12.0f) / 24.0f) * 2.0f * M_PI / 365.0f;
// equation of time (minutes)
float eqtime = 229.18f * (0.000075f + 0.001868f * cos(gamma) - 0.032077f * sin(gamma)
- 0.014615f * cos(2.0f*gamma) - 0.040849f *sin(2.0f * gamma));
// solar declination angle (radian)
float decl = 0.006918f - 0.399912f * cos(gamma) + 0.070257f * sin(gamma) - 0.006758f * cos(2.0f * gamma)
+ 0.000907f * sin(2.0f * gamma) - 0.002697f * cos(3.0f * gamma) + 0.00148f * sin(3.0f * gamma);
if (daylightsaving) timezone++;
float time_offset = eqtime - 4.0f * longitude + 60.0f * timezone;
// true solar time
float tst = hour * 60.0f + minute + sec / 60.0f + time_offset;
//solar hour angle (degrees)
float ha_deg = (tst / 4.0f) - 180.0f;
//solar hour angle (radian)
float ha_rad = ha_deg * M_DEGTORAD;
// solar zenith angle (radian) https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Solar_zenith_angle
float za_rad = acos(sin(lat_rad) * sin(decl) + cos(lat_rad) * cos(decl) * cos(ha_rad));
*elevation = 90.0f - za_rad / M_DEGTORAD;
// solar azimuth, clockwise from north
float az_rad = acos( (sin(lat_rad) * cos(za_rad) - sin(decl) ) / ( cos(lat_rad) * sin(za_rad) ) );
*azimuth = 180.0f - az_rad / M_DEGTORAD;
}
I not tested deeply the codes, just run a few times, but here is a site for test:
http://sunposition.info/sunposition/spc/locations.php#1